PVC Extruder Machine: Everything You Need to Know
In the world of plastic manufacturing, precision and efficiency are paramount. Whether you are producing construction materials or medical devices, the quality of your output depends heavily on your equipment. At the heart of this industry lies the pvc extruder, a workhorse capable of transforming raw resin into complex, usable shapes. At HZH Mould, we understand that mastering this technology is key to staying competitive.
What is a PVC Extruder Machine?
To understand the industry, you first need to answer the fundamental question: what is extruder machine technology? Essentially, a PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) Extruder Machine is a sophisticated piece of manufacturing equipment designed to melt raw plastic and form it into a continuous profile.
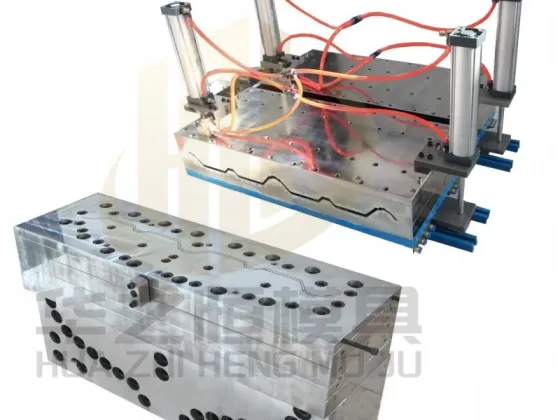
Unlike injection molding, which creates individual parts, a pvc machine operates on a continuous flow principle. Raw PVC is heated until it reaches a molten state and is then forced through a specialized die. As the material exits the die, it cools and solidifies into the final shape, such as a pipe, sheet, or film. This high-efficiency process allows manufacturers to control dimensions with incredible accuracy, ensuring consistency across massive production runs.
Understanding the PVC extrusion process
The journey from raw pellet to finished product involves a specific sequence of events:
Feeding: Raw PVC pellets or powder are gravity-fed into the machine's hopper.
Heating: As the material moves from the hopper into the barrel, external heaters and friction raise its temperature until molten.
Extruding: The liquid PVC is pushed through a precision-cut die, which dictates the profile's cross-section.
Cooling: Upon exiting the die, the profile enters a cooling bath (usually water or air) to lock in its shape.
Cutting: The continuous profile is cut to specified lengths.
Inspection: Final quality checks ensure the output meets HZH Mould’s rigorous standards.
The main components of a PVC extruder machine
A robust extrusion system relies on the synergy of several key components. Understanding plastics extrusion lines helps operators maintain efficiency:
Hopper: The entry point for raw materials.
Barrel: A distinctively lined cylinder equipped with heater bands to melt the PVC.
Screw: The "engine" of the process. Driven by a powerful motor, the screw mixes, shears, and conveys the molten plastic toward the die.
Die: The custom-tooling component that shapes the plastic.
Cooling System: Fans or water tanks that rapidly stabilize the hot plastic.
Controller: The brain of the operation, regulating temperature, pressure, and screw speed (RPM).
Types of PVC products manufactured using extruder machines
The versatility of the pvc extruder allows for a vast array of applications. By simply changing the die and downstream equipment, manufacturers can pivot between products.
Pipes and Tubes: Essential for plumbing and irrigation due to corrosion resistance.
Window Profiles: Specialized pvc window extruders are used to create energy-efficient window and door frames.
Architectural Moldings: For intricate designs, companies often seek grille housing plastic mold wholesale solutions to produce detailed WPC or PVC decorative elements.
Cable Insulation: Coating electrical wires for safety.
Medical Devices: Producing sterile tubing and IV bags.
The importance of PVC extruder machines in the plastic industry
The dominance of extrusion technology stems from its ability to handle high-volume production economically. It allows for the use of recycled PVC, promoting sustainability, and offers a lower cost-per-part compared to other molding methods. Furthermore, the ability to produce complex cross-sections makes it indispensable for the construction and automotive sectors.
Advantages and disadvantages of the PVC extrusion process
Advantages:
Material Efficiency: Minimal waste, as scrap can often be reground and reused.
High Output: Designed for continuous, 24/7 operation.
Flexibility: Cross-sections can be complex and varied.
Disadvantages:
Setup Costs: High initial investment for dies and calibration tables.
Material Limits: Not all polymers extrude well; PVC requires precise thermal stability.
Variance: Slight fluctuations in process conditions can impact the entire run's tolerance.
How Does a PVC Extruder Machine Work?
If you have ever asked, "how does extruder work?" the answer lies in a combination of heat, pressure, and friction.
The working principle of a PVC extruder machine
At its core, the machine uses a screw rotating inside a heated barrel. As the screw turns, it conveys the PVC pellets forward. The mechanical friction generated by the screw against the barrel wall provides a significant portion of the heat needed to melt the plastic, supplemented by external heaters. This molten plastic is then pressurized and pushed through the die, taking the shape of the final product.
Role of temperature and pressure in PVC extrusion
Temperature control is critical. If the PVC is too cool, it won't flow through the die; if it's too hot, the material will degrade and burn. Similarly, pressure must be maintained to ensure the material packs densely into the die, preventing voids and ensuring structural integrity. Consistent pressure ensures that the profile remains uniform throughout the production run.
Steps involved in the PVC extrusion process
To summarize the operational flow:
Feeding: Pellets enter the feed throat.
Conveying & Melting: The screw shears the material, melting it via friction and heater bands.
Pumping: The melt is pressurized near the end of the screw.
Shaping: Material flows through the die.
Sizing & Cooling: Vacuum calibration tables hold the shape while water cools it.
Pulling & Cutting: A haul-off unit pulls the profile at a constant speed before it is cut.
Common issues and troubleshooting in PVC extrusion machines
Even the best machines encounter hiccups. Here is how to handle them:
Die Swell: If the plastic expands upon exiting the die, try reducing the melt temperature.
Melt Fracture: Rough surfaces ("sharkskin") often indicate the extrusion speed is too high or the die is too cold.
Air Bubbles: Usually caused by moisture in the raw material. Ensure pellets are dry before feeding.
Overheating: PVC is heat-sensitive. Check your temperature controllers and screw speed immediately if discoloration occurs.
Maintenance tips for PVC extruder machines
To ensure longevity, regular maintenance is non-negotiable. Clean the screw and hopper regularly to prevent cross-contamination. Lubricate the gearbox and motor bearings to minimize wear. Most importantly, monitor your heater bands; a single failed band can cause uneven melting and ruin a production batch. Always follow the specific guidelines provided by your pvc extruder machine manufacturer.
Summary
The PVC extruder machine is a cornerstone of modern plastic manufacturing, offering a blend of efficiency, versatility, and precision. From understanding the complex interplay of temperature and pressure to selecting the right dies for pvc window extruders or specialized grille housings, mastering this technology is essential for success.
At HZH Mould, we combine two decades of industry experience with cutting-edge technology to support your production lines. whether you need high-quality molds or guidance on optimizing your extrusion parameters, we are here to help you achieve superior product quality and operational efficiency.

